Section 4: Sample Selected-Response Questions
TX PACT: Life Science: Grades 7–12 (738)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for you to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied by the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements do not appear on the actual exam.
The correct answer is provided for each sample exam question. The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will see on the exam; however, your performance on the sample questions should not be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual exam.
Domain I—Nature of Science
Competency 001—Understand principles and procedures of scientific inquiry.
1. A scientist would like to determine the effect of night length on the flowering of the mustard plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Thirty of these plants will be randomly assigned to each of three experimental groups. The best rationale for including 30 plants in each experimental group is to:
- minimize the effects of individual variations among the plants on the experimental results.
- allow more conditions to be varied at once for each group.
- reduce the chance that the scientist's expectations will influence the outcome of the experiment.
- provide a sufficient number of plants for a control group.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer 1.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the principles and procedures for designing and carrying out various types of scientific investigations. In sexually reproducing organisms, all individuals are genetically unique and thus vary in their characteristics. The inclusion of 30 plants in each experimental group, instead of just a few, provides a statistical measure of how much of the observed variation within a treatment group reflects individual variation among the plants rather than variation that is the result of the experimental treatment.
Competency 002—Understand the history and nature of science.
2. For which of the following reasons is the periodic table of the elements a useful model in science?
- It lists the elements in order of their percent abundance in Earth's crust and atmosphere.
- It organizes the elements into groups with shared chemical and physical properties.
- It provides a historical record of the order in which the elements were discovered.
- It separates the elements into three groups based on the state they are in at room temperature.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to identify unifying scientific theories, models, and concepts in biology, Earth and space science, chemistry, and physics. Each column in the periodic table of the elements represents a group of elements with the same number of valence, or outer shell, electrons. This means that all the elements in a column are capable of forming the same number of chemical bonds and exhibit similar chemical behaviors. Elements are placed into rows, or periods, according to the number of shells occupied by their electrons, and are arranged across the table by increasing total numbers of electrons and atomic weights.
Competency 003—Understand the relationships between biology, engineering, technology, mathematics, and society.
3. Which of the following advances in molecular biology has led to the most recent changes in vaccine development?
- the manufacturing of vaccines that contain live pathogenic agents
- the production of vaccines that allow transmission of lifelong immunity from one generation to the next
- the synthesis of vaccines that provide lifelong immunity
- the creation of vaccines composed of viral coat proteins that trigger immune responses
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the interrelationships between biology, engineering, technology, mathematics, and society. The ability to produce a vaccine composed only of viral coat protein antigens means that in the future vaccines could be genome-free. This reduces the risk of mutation to more dangerous viral forms that can occur in currently and previously available vaccines that consist of attenuated complete viruses.
Domain II—Biochemistry and Cell Biology
Competency 004—Understand the chemistry of living systems.
4. Which of the following best explains carbon's central role in the composition of biomolecules?
- Carbon exists as a solid at room temperature.
- Carbon's four valence electrons allow it to bond with other atoms in a wide variety of ways.
- Carbon is the element with the greatest electronegativity.
- Carbon's six protons make it easy for it to achieve an octet by reacting with the alkaline Earth metals.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of basic chemistry, including the characteristics of atoms and molecules, and of the physical and chemical properties of water and carbon and the biological significance of these properties. Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell and by sharing electrons forms stable single and double covalent bonds with a number of other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen. It is thus capable of forming large, complex molecules with skeletons that differ in their length, degree of branching, or arrangement in closed rings. This diversity in molecular structures makes possible the diversity of living organisms.
Competency 005—Understand cell structure, function, and bioenergetics.
5. Which of the following is most likely to occur when yeast cells have exhausted the supply of oxygen present in their growth medium?
- Lactic acid will accumulate in the lysosomes of the yeast cells.
- Fermentation will regenerate NAD+ positive, and glycolysis will continue.
- Carbon dioxide production will increase and acidify the medium.
- ATP production will cease, and the yeast cells will die.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. In the absence of oxygen that can serve as the final electron receptor, the end product of glycolysis, pyruvate, is converted to ethanol. This is accomplished by the reduction of acetaldehyde by NADH, thus regenerating a supply of NAD+ positive that can accept electrons during the oxidation step of glycolysis, and allowing that process to continue.
Domain III—Genetics and Evolution
Competency 006—Understand molecular genetics.
6. Which of the following is the most likely cause of a base pair mutation?
- Sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis.
- A small portion of one chromosome is added to another chromosome.
- A segment of a chromosome breaks, flips, and reinserts itself.
- The DNA is not accurately duplicated during replication.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the types and causes of chromosomal and gene mutations, the consequences of these genetic changes, and the genetic basis of common disorders and diseases. Mutations that involve nucleotide base pairs typically result from the substitution, insertion, or deletion of one or more incorrect bases. These most commonly occur during the replication of DNA when the new complementary strands are being produced.
Competency 007—Understand patterns and processes of inheritance.
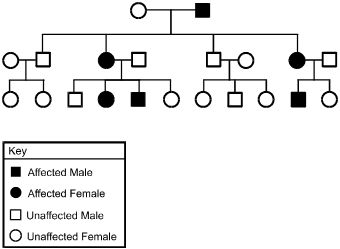
The key provides symbols for Affected Male, Affected Female, Unaffected Male, and Unaffected Female. In the first generation, an unaffected female crosses with an affected male. This pair produces 4 offspring, which from left to right are an unaffected male who crosses with an unaffected female, an affected female who crosses with an unaffected male, an unaffected male who crosses with an unaffected female, and an affected female who crosses with an unaffected male. The first pair from the second generation produces 2 unaffected females. The second pair produces an unaffected male, an affected female, an affected male, and an unaffected female. The third pair produces an unaffected female, an unaffected male, and an unaffected female. The fourth pair produces an affected male and an unaffected female.
7. The pedigree above shows the sex-linked inheritance pattern of a gene. This pattern of inheritance suggests the allele is:
- X-linked dominant.
- X-linked recessive.
- Y-linked dominant.
- Y-linked recessive.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze patterns of inheritance and the relationship between genotypic and phenotypic frequencies. The allele cannot be inherited as Y-linked, since females in the first generation of offspring express the trait. If the trait is X-linked recessive, the affected females of the first generation must be homozygous recessive and their offspring should show sex linkage, with the males affected and the females unaffected. This is not the case. The pattern in the pedigree is consistent with an X-linked dominant, however. The affected females of the first generation must be heterozygous for the trait so the expression of the trait in their offspring would not show sex linkage. This is the pattern in the pedigree.
Competency 008—Understand the mechanisms of biological evolution.
8. The occurrence of similar features in organisms from different phylogenetic lineages can be attributed to:
- gradualism.
- stabilizing selection.
- convergent evolution.
- uniformitarianism.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze evolutionary patterns and the mechanisms of speciation. Organisms that are only distantly related may adapt by developing similar characteristics in response to similar selective pressures. This is known as convergent evolution.
Competency 009—Understand the scientific explanations and evidence for the history of life on Earth.
9. Which of the following would provide the strongest evidence of a relatively close evolutionary relationship between two species?
- Both species occupy similar niches in their respective ecological communities.
- Fossils of ancestors of both species are found in the same geographic area.
- The embryos of both species look almost identical until late stages of development.
- Both species use the same 20 amino acids to synthesize peptides and proteins.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze different kinds of scientific evidence for evolution. Homologous patterns of development that appeared early are shared by all members of an evolutionary lineage. Homologies shared by some but not all members of a lineage suggest that the species sharing these homologies have a more recent common ancestor than other members of the lineage. Thus species whose embryos differ from each other only in the very late stages of development are likely to be more closely related to each other than species that diverged at earlier stages of development.
Domain IV—Biological Unity and Diversity
Competency 010—Understand the structures and functions of organisms and their life cycles.
10. The process of conjugation is significant in the bacterial life cycle because it allows:
- a bacterium to switch from being heterotrophic to autotrophic.
- deleterious mutations in a bacterium's genome to be corrected.
- a bacterium to make an exact duplicate of itself.
- genetic material to be transferred from one bacterium to another.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of viruses, prokaryotes, protists, and fungi, including their reproduction and life cycles. Conjugation in prokaryotes is the direct one-way transfer of DNA from one cell to another.
Competency 011—Understand how organisms obtain, store, and use energy and matter to maintain homeostasis.
11. Which of the following best describes how mushrooms and similar fungi obtain nutrients?
- The hyphae secrete enzymes that break down large molecules in the immediate environment and then absorb the smaller molecules.
- Cells in the hyphae engulf large food particles, forming food vacuoles that fuse with lysosomes so that digestive enzymes can break down the particles.
- Tubes formed by the hyphae transport food particles to specialized storage structures where the food is digested and the nutrients are absorbed.
- Hyphae periodically organize into structures that grow toward sunlight and produce nutrients by photosynthesis.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze how prokaryotes, protists, and fungi obtain, store, and use energy, nutrients, and water to maintain homeostasis. Unlike animals, fungi do not ingest their food before digesting it. Instead they secrete enzymes that break down complex organic molecules in the surrounding environment and then absorb the nutrients.
Competency 012—Understand the anatomy and physiology of human organ systems.
12. In many vertebrates, including humans, blood flows in two circuits in an arrangement called double circulation. Which of the following is an advantage of double circulation over the single circulation organization found in fish?
- There is greater surface area over which gas exchange between the blood and environment occurs, resulting in higher oxygen levels.
- Oxygenated blood can be mixed with deoxygenated blood before passing through the tissues of the body.
- The blood flows to the body tissues under higher pressure and faster, allowing for more efficient delivery of oxygen.
- Blood flow to different parts of the body can be regulated more precisely to meet localized oxygen needs.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the general structure, organization, function, and homeostatic relationships of the respiratory, circulatory, digestive, and excretory systems. Having a pulmonary circulation and pump that are separate from the systemic circulation and pump allows the systemic pump to repressurize the blood flow as it leaves the heart for the body's tissues. This increases the rate at which oxygen can be delivered to the tissues.
Domain V—Ecology and Environment
Competency 013—Understand populations and communities.
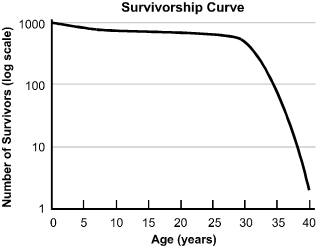
The horizontal axis is labeled "Age (years)" and has values marked from 0 to 40 in increments of 5. The vertical axis is labeled "Number of Survivors (log scale)" and has values marked at 1, 10, 100, and 1000, with the distance between each of the values the same. The curve begins at (0, 1000), descends gradually to approximately (32, 800), and then drops steeply to approximately (40, 2).
13. What does the survivorship curve shown above indicate about a population made up of individuals with an average life expectancy of 40 years?
- The greatest increase in survivorship occurs at the end of the lifespan.
- Members of the population are most vulnerable during infancy.
- The population has a low mortality rate during middle age.
- Individuals begin reproduction very early in the lifespan.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze demographic characteristics, life history patterns, population growth curves, and survivorship curves for populations occurring in different habitats and under different conditions. The graph shown is an example of a Type I survivorship curve, reflecting low death rates at early and middle ages and a steeper drop-off in old age.
Competency 014—Understand ecosystems and biomes.
14. Which of the following would most likely increase the amount of phosphorus available to organisms in an ecosystem?
- the burning of fossil fuels
- the rising of air temperature
- the cultivation of leguminous plants
- the weathering of rocks
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze energy flow and biogeochemical cycling in ecosystems. Of the possible responses, only the weathering of rocks would increase the availability of phosphorus to organisms because the largest reservoir of phosphorus is in sedimentary rocks of marine origin.
Competency 015—Understand the effects of human activities on the biosphere.
15. Scientists have observed reduced fertility in a variety of aquatic animals including fish, reptiles, and insects in waterways near urbanized or agricultural areas. This reduction in fertility rates is most likely a result of:
- an increase in the number of invasive species present in degraded habitats.
- a disruption of endocrine systems caused by the introduction of natural hormones and synthetic compounds.
- a decline in the quantity and quality of food resources needed to sustain reproduction.
- an interruption of mating behaviors and the destruction of breeding sites caused by human activity.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the effects of human activities on the atmosphere and climate and the implications of these effects for humans and other organisms. The introduction of endocrine disrupters into wetlands and waterways negatively affects the reproduction, growth, and development of wildlife, especially carnivorous animals. Widely publicized examples of endocrine disrupters include DDT and PCBs, but human medicines and cosmetics are now also known to interfere with the functioning of hormones and endocrine glands in seals, fish, alligators, and snails, for example.