Preparation Manual
Section 4: Sample Selected-Response Questions
TX PACT: Physical Education: Early Childhood–Grade 12 (758)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for you to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied by the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements do not appear on the actual exam.
The correct answer is provided for each sample exam question. The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will see on the exam; however, your performance on the sample questions should not be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual exam.
Domain I—Growth and Motor Development
Competency 001—Understand stages and characteristics of human growth and development.
1. Which stage of development is typically characterized by slow and steady physical growth, refinement of fundamental motor skills, and the ability to think in concrete operational terms?
- the early childhood years (ages 2 to 6)
- the middle childhood years (ages 6 to 11)
- the early adolescent years (ages 11 to 15)
- the later adolescent years (ages 15 to 18)
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of stages and characteristics of human growth and development. The middle childhood stage of physical development is characterized by slow, steady growth and improvement and refinement of motor skills. Cognitively, children are said to be in the concrete operational stage, which Piaget defined as the capacity to engage in mental operations or internalized actions that fit into a logical system. Children carry out these mental operations in the presence of the concrete objects and events being thought about.
Competency 002—Understand concepts and principles of anatomy and physiology as they relate to movement and physical fitness.
2. At the onset of puberty, the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to release growth hormone and stimulate the production of thyroxine. The increase in these two substances, which causes gains in body size and skeletal growth, results primarily from the interaction of which two body systems?
- the muscular system and the skeletal system
- the circulatory system and the integumentary system
- the nervous system and the endocrine system
- the respiratory system and the reproductive system
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to distinguish between functions, actions, and physiological processes of body systems. The brain, part of the central nervous system, houses the hypothalamus, which regulates the endocrine system, including the thyroid and pituitary glands. When thyroxine levels are low, the hypothalamus secretes a releasing hormone that stimulates the pituitary to secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyroid to secrete thyroxine. Thyroxine stimulates metabolic rate and influences protein production, which affects the growth rate of children. The anterior lobe of the pituitary secretes somatotropin or growth hormone (GH), which stimulates bone and muscle growth.
Competency 003—Understand principles, sequences, and characteristics of motor development and motor learning.
3. In the context of motor learning, the concept of readiness refers to the:
- combination of maturation and experience that allows an individual to learn and acquire a new motor skill.
- ability of an individual to alter motor behaviors in order to adjust to changing demands in a learning environment.
- capacity of human biology, as in neural and bone development, to reorganize and respond to a motor challenge or injury.
- interplay of environmental factors that results in favorable or ideal conditions in which to learn a new motor skill.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to recognize concepts and principles of motor learning. The concept of readiness relates to factors that affect an individual's ability to acquire a motor skill. Readiness is primarily determined by the biological maturity of the learner (the learner's level of physical growth and motor development) and the learner's experience (the way in which practice conditions and the motor learning environment affect how the skill is learned). According to motor learning principles, when a motor learning activity is appropriate for the physical, cognitive, and emotional development of students and environmental conditions are favorable, learners will gain proficiency in new motor skills.
Domain II—Movement Activities
Competency 004—Understand fundamental movement concepts and skills and principles of biomechanics.
4. During a soccer unit, a physical education teacher provides cues to promote students' efficiency in skill execution. For example, for passes, the teacher reminds students to place their nonkicking foot alongside the ball with toes pointed at the target to help create velocity in the kicking foot and improve accuracy. To increase the distance of throw-ins, the teacher tells students to bring the ball back behind their heads with elbows bent, and then flex their trunk and extend their arms forcefully and directly overhead on the release. This approach is most closely aligned with which of the following national standards for physical education?
- Achieves and maintains a health-enhancing level of physical fitness.
- Demonstrates competency in motor skills and movement patterns needed to perform a variety of physical activities.
- Demonstrates understanding of movement concepts, principles, strategies, and tactics as they apply to the learning and performance of physical activities.
- Exhibits responsible personal and social behavior that respects self and others in physical activity settings.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to apply knowledge of movement concepts and biomechanical principles in the context of movement activities. In this scenario, the physical education teacher demonstrates how to integrate Standard 2 of the National Standards for Physical Education, "Demonstrates understanding of movement concepts, principles, strategies, and tactics as they apply to the learning and performance of physical activities," into an instructional activity. By pointing out how to use body mechanics to improve velocity and accuracy in passing and distance in throw-ins in soccer, the teacher illustrates for students how knowledge of biomechanical concepts and movement principles can be used to develop efficiency in skill execution.
Competency 005—Understand principles, techniques, skills, activities, organizational strategies, and safety practices for sports and recreational activities.
5. In a game of volleyball, a "bump" or forearm pass is the most appropriate technique to use to:
- spike the ball over the net.
- play a ball that arrives low and with force.
- receive a ball off of the net.
- return a ball that arrives at chest height or higher.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to identify techniques for executing complex sport skills. In volleyball, a forearm pass, or "bump," is recommended for playing a ball that arrives with force below chest level and is often used to receive serves and spikes. In the forearm pass, a player extends the arms in front of the body and joins hands, keeping hands and wrists together. The elbows rotate in so that the widest portion of each forearm faces upward. The elbows are locked on contact and the ball is contacted between the wrists and elbows.
Competency 006—Understand principles, techniques, skills, activities, organizational strategies, and safety practices for rhythmic movement and dance; stunts, tumbling, and educational gymnastics; and cooperative, group, and adventure activities.
6. Parachute play contributes to the development of skills important for dance by encouraging students to focus on:
- visual clues for recognizing a rhythm.
- shaping movement to mirror shapes created by others.
- the ways in which movement can express an idea.
- coordinating movement timing with the movement of others.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to recognize activities that promote development of rhythmic movement and dance skills. In parachute play, students manipulate a nylon parachute as a group, lifting and lowering it to make ripples and domes, and moving clockwise and counterclockwise in a circle while keeping it inflated. These activities, especially when accompanied by counting or a musical cadence, promote students' ability to move in unison and to coordinate the timing and flow of their movements with the movements of others. These skills are transferable to many forms of dance, including line and social dance, which require participants to move to a rhythm in a synchronized way with others.
Domain III—Lifelong Physical Fitness
Competency 007—Understand principles and components of health-related physical fitness, including activities for promoting cardiorespiratory endurance, flexibility, muscular strength and endurance, and body composition.
7. 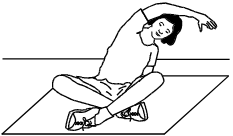
In the exercise shown above, the student's arm is down to the side with the hand slightly behind the body for support.
The other arm extends overhead and reaches to the opposite side. The stretch is held briefly. The student repeats the
movement with the other arm. This stretch targets which of the following muscles?
- biceps
- erector spinae
- gluteus maximus
- latissimus dorsi
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to recognize techniques and activities for developing and improving flexibility of the joints and muscles. The latissimus dorsi, a wide powerful muscle, arises from the lower vertebral column, covers the lower back, and runs from the side of the trunk to the humerus. The action of the latissimus dorsi draws the upper arm downward and backward and rotates it inward. In the flexibility exercise illustrated, the participant stretches one arm overhead while bending at the waist in the same direction, thereby stretching the side of the trunk where the latissimus dorsi is located. To stretch the other latissimus dorsi, the participant switches arms to stretch the other side of the trunk.
Competency 008—Understand principles, procedures, and resources for developing and maintaining physical activity/fitness and weight management plans.
8. Which of the following strategies is likely to be most effective for supporting an adolescent's efforts to lose weight?
- having regular family meal and snack times
- sending the adolescent to school with homemade lunches instead of lunch money
- involving the entire family in a healthy eating plan
- reminding the adolescent frequently of the health risks prevented by losing weight
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to recognize sound weight management principles and practices and strategies for integrating them into daily life. Family involvement and encouragement are key to supporting an adolescent's efforts to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight. An adolescent is much more likely to be motivated and committed to healthful eating if his or her family participates in and reinforces the behavior. Strategies such as modeling healthy eating habits and preparing meals that provide the proper balance of nutrients from a variety of foods are essential for establishing sound family nutritional practices.