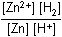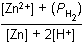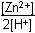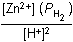Preparation Manual
Section 4: Sample Selected-Response Questions
TX PACT: Chemistry: Grades 7–12 (740)
Expand All Answers | Collapse All Answers
This section presents some sample exam questions for you to review as part of your preparation for the exam. To demonstrate how each competency may be assessed, sample questions are accompanied by the competency that they measure. While studying, you may wish to read the competency before and after you consider each sample question. Please note that the competency statements do not appear on the actual exam.
The correct answer is provided for each sample exam question. The sample questions are included to illustrate the formats and types of questions you will see on the exam; however, your performance on the sample questions should not be viewed as a predictor of your performance on the actual exam.
The following reference materials will be available to you during the exam:
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Domain I—Nature of Science
Competency 001—Understand principles and procedures of scientific inquiry.
1. Which of the following is best accomplished using a mass spectrometer?
- determining the percent abundance of an element's natural isotopes
- determining the triple point of an unknown substance
- determining the reaction rate for a chemical reaction involving a gas
- determining the electronegativity value of an element
- Enter to expand or collapse answer 1.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the equipment used in chemistry. A mass spectrometer measures the masses and relative abundance of atomic or molecular ions in a sample. These numerical values can be used to calculate the percent abundance of an element's natural isotopes.
Competency 002—Understand the history and nature of science.
DNA → RNA → protein2. Which of the following biological processes does the pathway shown above summarize?
- mitosis
- cellular respiration
- meiosis
- gene expression
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of major contemporary concepts in biology. DNA is a molecule that stores genetic information in cells. The pathway shows the translation of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein, a process that leads to the active expression of genetic information.
Competency 003—Understand the relationships among science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and society.
Flexible polyurethane foams are used in many commercial products, such as upholstered furniture, bedding, automobile seats, and sponges. An important component in the manufacturing of flexible polyurethane foams are polyols, which are typically derived from petroleum products. In 2007, Cargill, Incorporated, was awarded a Presidential Green Chemistry Challenge Award from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for its research into polyols made from renewable biological resources. The quality and performance of the polyurethane foam made from these non-petroleum-based polyols proved comparable to the quality and performance of the polyurethane foam made from petroleum-based polyols.
3. The passage above illustrates which of the following about the relationships among science, technology, and society?
- Private industry is reluctant to comply with EPA standards without strict government oversight.
- Chemistry research can play a significant role in solving major environmental problems.
- Environmentally friendly technologies can only be competitive with government support.
- Applied chemistry research is increasing due to a decrease in public funding for basic research.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the interrelationships among science, technology, and society. Knowledge of chemistry can be used to assess existing manufacturing protocols and to propose alternative procedures. These new procedures can play a significant role in mitigating the environmental problems facing society.
Domain II—Matter and Atomic Structure
Competency 004—Understand the properties of matter.
4. Which of the following only occurs during a nuclear change?
- Valence electrons are raised to higher energy levels.
- Two or more types of atoms are combined.
- Energy is released to the surroundings.
- An element's atomic number is reduced.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of radioactive materials. Chemical and physical changes do not involve changes within the nucleus of an atom and therefore would not lead to a reduction in an element's atomic number. This type of change would only result from a nuclear change.
Competency 005—Understand atomic theory and the periodic table.
5. Which of the following elements is the most electronegative?
- hydrogen
- fluorine
- radon
- francium
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the periodic table and its usefulness in predicting the relative reactivity of given elements. The electronegativity of elements in the periodic table tends to increase from bottom to top within a group and from left to right across a period. Of the given elements, fluorine is in the uppermost position on the right-hand side of the periodic table.
Competency 006—Understand the kinetic molecular theory, the nature of phase changes, and the gas laws.
6. A gas occupies a volume of 1.25 liters at a pressure of 825 mm Hg. What will be the final pressure of this gas if it is compressed into a volume of 725 mL at constant temperature?
- 479 mm Hg
- 748 mm Hg
- 1.30 times 10 cubed mm Hg
- 1.42 times 10 cubed mm Hg
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to solve a problem involving the gas laws. If the temperature and number of moles of a gas are held constant, the relationship between initial pressure and initial volume and a new pressure and a new volume is P subscript 1 V subscript 1 equals P subscript 2 V subscript 2. This relationship can be used to calculate the new pressure when the initial pressure, initial volume, and new volume are known.
Domain III—Energy and Chemical Bonding
Competency 007—Understand the principles of thermodynamics and calorimetry.
7. A 4.75 g sample of solid NaOH is dissolved in 50.5 g of H2O in a constant-pressure calorimeter having a heat capacity of 18.5 joules per degrees Celsius. The temperature rises from 21.1 degrees Celsius to 33.6 degrees Celsius. Assuming that the solution has a specific heat capacity of 4.184 joules per gram per degrees Celsius and negligible heat loss from the calorimeter, how much heat is produced in the solution process?
- 2.64 kJ
- 2.89 kJ
- 3.12 kJ
- 4.27 kJ
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze the results of a calorimetry experiment. The total heat produced in the given solution process is equal to the heat absorbed by the solution plus the heat absorbed by the calorimeter. The heat absorbed by the solution is calculated using the equation q equals m times s times Delta T. The heat absorbed by the calorimeter is equal to C subscript calorimeter times Delta T.
Competency 008—Understand energy relationships in chemical bonding, chemical reactions, and physical processes.
| Bond | Bond Enthalpy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| H—H | 436.4 |
| H—Cl | 431.9 |
H2(g) plus Cl2(g) right arrow 2HCl(g) new line Delta H degrees subscript rxn equals negative 184.6 kJ
8. Given the information shown above, what is the best estimate of the bond enthalpy for the Cl—Cl bond?
- 189.1 kJ/mol
- 242.8 kJ/mol
- 256.3 kJ/mol
- 585.1 kJ/mol
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze energy changes due to the formation or breaking of chemical bonds. The enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes involved in breaking existing bonds minus the sum of the enthalpy changes involved in forming new bonds. The bond enthalpy for the Cl—Cl bond can be calculated using this relationship and the given bond enthalpies for H—H and H—Cl.
Competency 009—Understand the nomenclature and structure of inorganic and organic compounds.
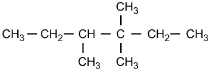
9. Which of the following structural formulas represents 4–ethyl-3, 3–dimethylhexane?
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to apply the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) rules of nomenclature. 4-ethyl-3, 3-dimethylhexane is an alkane consisting of six continuous carbon atoms. An ethyl group (C2H5) is attached to the number 4 carbon and two methyl groups (CH3) are attached to the number 3 carbon.
Competency 010—Understand chemical bonding and intermolecular forces and their effect on the properties of substances.
10. The high melting point of diamond is due to:
- strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
- an irregular, three-dimensional crystal structure.
- delocalized, highly mobile bonding electrons.
- extensive van der Waals forces between carbon atoms.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to relate the properties of substances to their atomic bonds. Diamond is a covalent-network crystalline solid. The carbon atoms in this network are linked by covalent bonds. This strong bonding between carbon atoms is responsible for the high melting point of diamond.
Domain IV—Chemical Reactions
Competency 011—Understand the nature of chemcial reactions.
11. Which of the following products is formed by an esterification reaction between acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH)?
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze different types of chemical reactions. In the esterification reaction between acetic acid and ethanol, the O H group from acetic acid and the H attached to the O in ethanol combine to form water. The remaining portions of the acetic acid and ethanol molecules combine to form the ester, ethyl acetate.
Competency 012—Understand the principles of chemical equilibrium.
Zn left parenthesis s right parenthesis plus 2H positive left parenthesis aq right parenthesis equilibrium arrow Zn superscript 2 positive left parenthesis aq right parenthesis plus H2 left parenthesis g right parenthesis12. Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the equation shown above?
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option D is correct. This question requires the examinee to solve problems involving equilibrium constants. When writing equilibrium constant expressions, pure solid and pure liquid compounds are omitted and the pressure of gaseous compounds can be used in place of concentration. The equilibrium constant expression for this reaction is equal to the concentration of Zn superscript 2 positive left parenthesis aq right parenthesis times the pressure of H2 left parenthesis g right parenthesis each raised to a power equal to its stoichiometric coefficient, divided by the concentration of H superscript positive left parenthesis aq right parenthesis raised to a power equal to its stoichiometric coefficient.
Competency 013—Understand acid-base chemistry.
13. Which of the following explains why nitric acid (HNO3) is a stronger acid than nitrous acid (HNO2)?
- The additional oxygen present in nitric acid increases the polarity of the O—H bond.
- The extent of ionization is directly related to molecular weight when comparing related compounds.
- The anion formed by removing H positive from nitrous acid is more stable than the anion formed by removing H positive from nitric acid.
- The O—H bond in nitrous acid is weaker than the O—H bond in nitric acid.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the relationship between molecular structure and acid strength. The strength of an acid is a function of its tendency to ionize. For oxoacids with the same central atom, acid strength increases as the oxidation number of the central atom increases because of the resulting increase in polarity of the O—H bond. The oxidation number of nitrogen in HNO3 is positive 5 and in HNO2 it is positive 3, thus the O—H bond in HNO3 is more polar and ionizes more readily.
Competency 014—Understand oxidation-reduction reactions and electrochemistry.
14. Automobile mechanics measure the density of the electrolyte solution of lead storage batteries to determine the amount of charge remaining. Which of the following statements describes the cause of the change in electrolyte density as the battery's charge decreases?
- The sulfuric acid electrolyte is consumed and water is formed.
- Water evaporates and the electrolyte concentration increases.
- The lead and lead left parenthesis IV right parenthesis oxide migrate from the solution to the electrodes.
- Lead in the electrolyte solution precipitates out of the solution.
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option A is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the applications of electrochemistry. During the normal operation of a lead storage battery, sulfuric acid is consumed and water is produced. The density of the electrolyte solution is related to how much of each of these substances is present in the solution.
Domain V—Stoichiometry and Solutions
Competency 015—Understand the mole concept.
15. Which of the following is equivalent to 1.42 times 10 to the power of 23 atoms?
- 25.0 g Br
- 15.0 g Cu
- 19.0 g Sn
- 23.0 g Mn
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to demonstrate knowledge of the mole concept. The number of moles of an element is equal to the product of the mass of the element divided by the molar mass of the element times Avogadro's number.
Competency 016—Understand stoichiometry.
N2 left parenthesis g right parenthesis plus 3H2 left parenthesis g right parenthesis right arrow 2NH3 left parenthesis g right parenthesis16. Given the equation shown above, how much NH3 is formed when 823 g of N2 are combined with 145 g of H2?
- 58.8 g
- 96.7 g
- 815 g
- 1650 g
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option C is correct. This question requires the examinee to solve stoichiometric problems involving mass. By calculating the number of moles of each reactant and analyzing the stoichiometric relationship between them, H2 can be identified as the limiting reactant. From the stoichiometric relationship between H2 and NH3, the number of moles of product formed can be calculated. This mole quantity can then be converted into mass using the molar mass of NH3.
Competency 017—Understand the properties of solutions and colloidal suspensions.
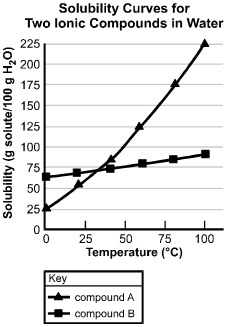
The horizontal axis is labeled Temperature in degrees centigrade, and has values marked from 0 to 100 in increments of 25. The vertical axis is labeled "Solubility (g solute/100 g H sub 2 O)", and has values marked from 0 to 225 in increments of 25. The curve for compound A passes through the following data points (values are approximate): (0, 25); (20, 55); (45, 80); (55, 125); (80, 175); and (100, 225). The curve for compound B passes through the following data points (values are approximate): (0, 65); (20, 70); (45, 75); (57, 77); (80, 80); and (100, 90).
17. Based on the solubility curves shown above, which of the following procedures will be most effective in isolating the greatest amount of pure compound A from a mixture consisting of 200 g of compound A and 15 g of compound B?
- dissolving the mixture in 100 g of water and then heating to the solution's boiling point
- dissolving the mixture in 100 g of water at 100 degrees Celsius and then decreasing the temperature to 0 degrees Celsius
- dissolving the mixture in 100 g of water at 75 degrees Celsius, filtering the solution, and then retaining the filtrate
- dissolving the mixture in 100 g of water and then slowly increasing the temperature to 100 degrees Celsius
- Enter to expand or collapse answer.Answer expanded
- Option B is correct. This question requires the examinee to analyze solubility curves. Based on the solubility curves provided, both compound A and compound B will be completely in solution when dissolved in 100 g of water at 100 degrees Celsius. As the temperature of the solution is decreased to 0 degrees Celsius, 175 g of compound A will come out of the solution, while all of compound B will remain in the solution. This is the procedure that yields the greatest amount of pure compound A.
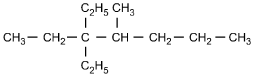
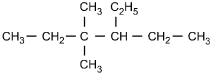
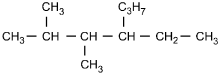
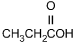
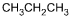
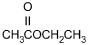
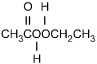
 Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)
Zn2+(aq) + H2(g)